- » Aims, Scope, Audience
- » Section Policies
- » Publication Frequency
- » Open Access Policy
- » Peer Review
- » Publication Ethics & Malpractice
- » Abstracting & Indexing
- » Archiving
- » Ethical Oversight
- » Publication Fees
- » Disclosing Interest
- » Plagiarism
- » Post-Publication Discussions and Corrections to Published Articles
- » Preprint and Postprint Policy
- » Data Access & Reproducibility
- » Advertising Policy
- » Direct Marketing
- » AI Technologies
Aims, Scope, Audience
"Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine" (hereinafter referred to as the Journal) is a peer-reviewed open access medical journal, which is the official publication of the "Russian Association of Gerontologists and Geriatricians" and is endorsed by the "Russian Gerontological Scientific and Clinical Center" of Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University.
The aim of the Journal is to provide the target audience with multidisciplinary up-to-date information about prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care of elderly patients, modern technologies for managing aging processes and geriatric syndromes, preserving and supporting the functional status of an elderly person, to deliver information about the achievements of gerontology and geriatric medicine, and clinical guidelines in this area.
The target audience: geriatricians, therapists, general practitioners; other participants in the geriatric link (nurses, social workers, teachers); researchers in the field of aging and related sciences; specialists working in borderline specialties (endocrinology, urology, gynecology, rheumatology, rehabilitation, cardiology, neurology, orthopedics and traumatology, etc.); heads of healthcare and medical institutions; students, residents and postgraduates.
Types of research welcomed and accepted
The Journal gives preference to clinical research (original research, case reports, reviews) with a geriatric focus in such areas as: internal medicine, endocrine diseases, nutrition, pharmacology, cardiovascular diseases, frailty and sarcopenia, neurodegenerative diseases, perioperative management and special care of the elderly, and rehabilitation.
As an exception, the Journal considers manuscripts in the field of basic sciences, including the biology of aging, experimental studies with animal models, as well as in the field of social sciences. Since the Journal welcomes open scientific and clinical discussion, it also encourages comments on published articles (especially for articles of the "Editor's Choice") and responses from authors of original publications to them.
Subject areas covered by the Journal:
Basic and clinical research
- Metabolism
- Nutrition and aging
- Reproductive aging
- Longevity
- Comparative aging
- Translational and clinical research
- Drug screening of anti-aging chemicals and pharmacology
- Artificial intelligence and technology
Age-related diseases
- Geriatric medicine
- Geroscience
- Immunology and inflammaging
- Arthritis
- Cardiovascular disorders
- Cancer
- COPD
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Dementia and neurodegenerative disorders
- Sensory decline
- Psychiatry
- Osteoporosis
- Frailty
- Sarcopenia
Health and social sciences
- Public and global health
- Physical, mental and social well-being
- Gerontology
- Public policy
- Psychology
- Sociology
- Demography
- Health economics
- Healthcare systems
Medical education and care improvement
- Information management
- Acute or subacute care
- Rehabilitation
- Nursing homes
- Primary care
- Ambulatory assessment
Section Policies
Publication Frequency
- Quarterly
Journal publication schedule
Issue number | Month of publication | Date of publication online |
No. 1 | March | End of March |
No. 2 | June | End of June |
No. 3 | September | End of September |
No. 4 | December | End of December |
Open Access Policy
All articles are freely available under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
The Journal supports most international initiatives in open access (esp. to research data and meta-data) including the Barcelona Declaration on Open Research Information for open access to research data, and encourages authors to post research data both in online supplements to the articles or in public repositories.
Peer Review
The Journal complies with the following basic principles:
- The peer review policy in the Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine is intended to meet the best practices and ethical standards set out in the recommendations of COPE, ICMJEand WAME, as well as the accepted industry definitions.
- DOUBLE BLIND review is used (reviewers do not know the identity of the authors, including their affiliations, and the authors do not know the reviewers).
- Blinding is performed by the responsible editorial office secretary.
- Double-blind peer review is also used for manuscripts by members of the editorial board.
- Number of reviewers: minimum 2 reviewers (for original research and reviews).
- Exceptions:
- Manuscripts by members of the editorial board
- News, editorial materials, interviews, comments on published articles and responses to them, as well as original research data posted in online appendices to the manuscript are not subject to peer review. However, all materials are checked by the editorial board.
- Authors may propose up to 5 reviewers (names and email addresses) themselves, provided that they are not affiliated with the authors' affiliation. However, the final decision on the selection of a particular reviewer is made by the editor-in-chief.
- Review is carried out by the of the editorial board members, as well as ин invited reviewers (leading experts in the relevant scientific field in Russia and other countries). A mandatory requirement for an invited reviewer is a position of academic degree.
- Each reviewer has the right to refuse to review in the event of an obvious conflict of interest that affects the perception and interpretation of the manuscript materials.
- Reviewing is done free of charge.
- The maximum expected number of reviews from members of the editorial board is no more than 3 reviews per year. External reviewers who have submitted more than 3 reviews per year are considered as candidates for inclusion in the editorial board of the Journal.
- Reviewing is designed to establish the compliance of manuscripts with the stated journal’s aims & scope.
- Manuscripts are checked for scientific novelty and clinical significance, the absence of plagiarism, the correctness of statistical analysis, clarity and understandability of presentation, as well as compliance with all ethical standards in the field of biomedical research. Other goals include supporting transparency, reproducibility, and data sharing (including proper registration of clinical trials).
- The review is conducted according to the internal form and checklist of the reviewer and members of the editorial board, which require a detailed, reasoned presentation, the necessary information on the terms and conditions of scientific review, the confidentiality regime and the protection of personal data (including GDPR), etc.
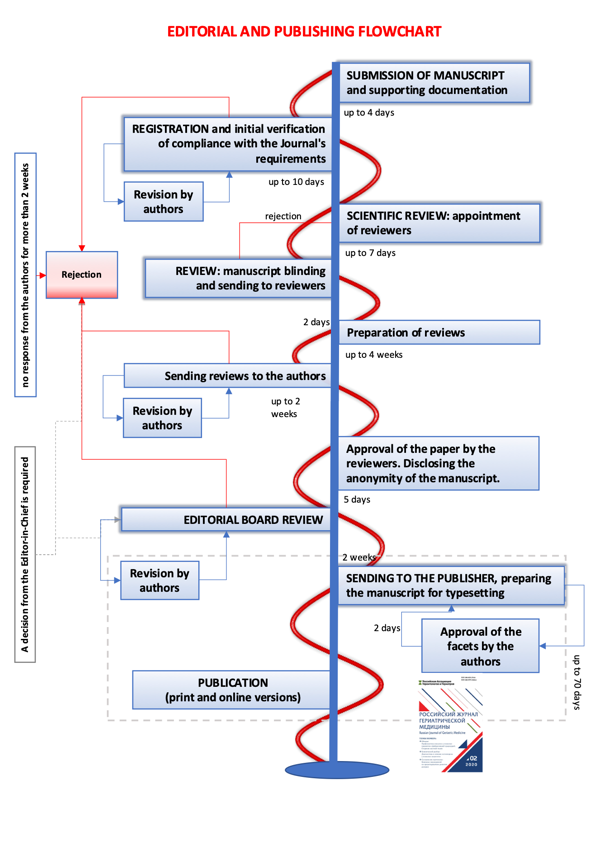
- If, due to the fault of the editors, the time frame for Reviewing a manuscript exceeds the time set in the flow chart by 1.5 times, the author has the right to withdraw his manuscript by notifying the editors in advance (in 7 working days).
- As part of the author's disagreement with the decision of the editorial board, the author has the right to send a written, reasoned claim (once per manuscript). The editorial board is obliged to review it no later than 3 weeks and to make a final decision, which is not subject to revision.
- The publisher/ founder does everything possible to train the editorial board and to keep it abreast of the current industry standards & updates.
Key editorial and publishing metrics
- Initial manuscript screening — less than 10 days
- 14 days from manuscript submission to the first decision
- First review period — less than 4 weeks
- Automatic manuscript rejection period in case of nor feedback from authors — 14 days
- Average period from manuscript submission to acceptance — 80 days.
- Review shelf life: 5 years
Editorial & publishing flow-chat
Publication Ethics & Malpractice
Authorship and contribution
The Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine adheres to the following criteria for authorship (developed and described in the ICMJE guidelines):
- Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work
- Drafting the work or reviewing it critically for important intellectual content
- Final approval of the version to be published
- Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Apart from being accountable for the parts of the study performed on their own, an author should be able to identify which co-authors are responsible for specific other parts of the work.
In addition, the authors should have confidence in the integrity of the contributions made by their co-authors. All those designated as authors should meet all four criteria for authorship, and all who meet the four criteria should be identified as authors.
COPE lists the following types of false authorship:
- Ghost authorsare authors who meet the criteria for authorship but are not listed as authors.
- Guest authorsare authors who do not meet accepted authorship criteria but are listed because of their rank, reputation, or perceived influence to make the publication appear more impressive.
- Gift authorsare authors who do not meet accepted authorship criteria, but are listed through personal relationship for mutual CV enhancement (including colleagues in articles in return for being listed in theirs).
Author and non-author contributions
Those who do not meet all four ICMJE criteria should be included in the Acknowledgements section as contributors. In case of such acknowledgent, the editorial staff should make sure that the contributors have given the corresponding author their consent to being acknowledged.
Author contribution statement. To indicate the contribution of each author, we recommend using the standardised Contributor Roles Taxonomy (CRediT).
It is the responsibility of the authors to ensure that the authorship and author contribution standards are met. The authors are obliged to provide transparent and correct information about themselves and the persons who made significant contributions to their study.
Authorship declaration
The editorial staff expects the authors to confirm the following in their cover letter signed by all co-authors.
By signing the declaration, the authors guarantee that:
- Each author signing the declaration meets the authorship criteria as outlined in Publication ethics;
- All individuals who participated in the study but are not the authors are specified as contributors in the Acknowledgements section;
- Each author’s contribution is described (this information will be published in Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine);
- The organisations and individuals mentioned in the Acknowledgements section have consented to their contribution to the manuscript being acknowledged.
Upon receipt of a manuscript, the editorial staff will verify that the authorship information and all the required documents are in place. In the absence of the authorship declaration or signatures from all the authors, the manuscript will not be accepted for consideration.
Disputes
In case of authorship dispute, the work on the article will be terminated regardless of the stage of its submission, reviewing, editing, or preparation for printing.
All the co-authors will be informed about the authorship dispute via e-mail.
The editors of the journal are entitled to set a precise deadline for the authors to provide clarification on the issues specified by the editors. Upon expiry of this period, the publication process is discontinued for this manuscript with an appropriate explanation. If an article has been published as an Online-First version, the clarification on withdrawal of the article from publication will be placed in the public domain.
In the case of a dispute regarding a published article, the editors of the journal will publish a correction, refutation, or retraction notice, explaining the reasons for correction, refutation, or retraction, respectively.
If it is necessary to add or remove a co-author before or after publication, the editors act in accordance with the COPE guidelines:
To prevent authorship problems, the editors use COPE flowcharts to identify the following warning signs:
- Industry funded research with no authors from the sponsor company, as these may require the editors to take a closer look at the authors’ contributions and, if necessary, to request explanations from the corresponding author;
- Co-authors list known to be from unrelated research areas, as this may indicate guest authorship;
- Unspecified roles in the Acknowledgements section;
- Questionable roles of contributors (for example, if no one appeared to draft the manuscript or to analyse the data);
- Authorship changes during pre-publication stage without notifying the editorial staff;
- Corresponding authors unable to respond to reviewers’ comments.
Complaints and appeals
The Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine carefully considers complaints about the behaviour of editors and peer reviewers, which may relate to issues such as a breach of confidentiality, an undisclosed conflict of interest, or a misuse of confidential information obtained during the peer-review process. The authors may also disagree with decisions regarding expressions of doubt on certain articles and complain about non-compliance with the editorial policies.
Complaints should be emailed to info@geriatr-news.com for consideration according to the standard procedure. Normally, complaint handling takes no more than 7 days. The editorial staff will inform the complainant of the decision, as well as of the corrective actions initiated and the deadlines for their implementation.
The editorial staff adhere to the COPE Guidelines for handling complaints in each of the following cases:
- Handling of post-publication critiques,
- Post-publication discussions and corrections,
- Peer-review manipulation suspected after publication,
- Image manipulation in a published article,
- Fabricated data in a published article.
If the authors do not agree with the decision of the Editorial Board, they may file a written reasoned complaint (once per manuscript). The editorial staff is obliged to consider the complaint within 3 weeks and make a final decision, which is not a subject to review.
Abstracting & Indexing
The Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine is included in the "List of leading peer-reviewed scientific journals and publications in which the main scientific results of dissertations for the degree of candidate of sciences, for the degree of doctor of sciences ..." (Higher Attestation Commission List) should be published.
Russian and international abstract and full-text databases also index articles published in the journal:
Archiving
- Russian State Library (RSL)
- National Electronic-Information Consortium (NEICON)
- Scientific Electronic Library elibrary.ru
Ethical Oversight
At Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine, we share COPE’s view that publication ethics includes not only ensuring the integrity and reliability of published research but also ethical behaviour towards research subjects. Ethical oversight should include policies on publication on vulnerable populations, ethical conduct of research using animals or human subjects (in the corresponding cases), handling confidential data and ethical business/marketing practices.
Informed consent and consent for publication
An informed consent/consent for publication form signed by patients (or their legal representatives) is required for every study in which one or several persons can be identified. This requirement also applies when a report involves deceased persons. Consent is required for the publication of photographs, medical histories, or other patient data, by which an individual or a group of individuals can be identified.
The authors are required to provide the editorial staff with a statement reporting that informed consent has been obtained from the patients or their legal representatives. The published article must inform that such consent has been obtained.
The informed consent for publication should include the following:
- The patient should fill in their name and sign the form.
- If a patient is unable to do so, the relationship of the signer to the patient must be stated.
- If one person is signing for a family or a group of people, that person should attest that all the members of the family/group have been informed.
- It should be stated that the person or group of persons has no legal, mental, or physical impediment to consent to publication. If such impediments exist, they should be stated (minor age, incapacity, disability, death).
- Consent forms should make it clear that, even if all the rules are followed, the journal cannot guarantee confidentiality.
- The patient should be informed that they may revoke consent at any time before the publication of the article.
- The consent form should indicate how the article will be distributed (in print, online).
- The consent form should contain a clause on whether the patient should read and approve the final version of the manuscript.
Vulnerable populations
The journal supports COPE’s position statement on the publication of studies involving vulnerable groups and individuals.
Vulnerable populations include (but are not limited to) pregnant women, neonates, children, foetuses, prisoners, physically handicapped, mentally challenged, economically disadvantaged, institutionalised and very sick patients, etc.
A study must be planned in vulnerable populations only if that population will benefit from this study.
One of the important points of concern in vulnerable populations is that some lack the ability to consent or understand. In that case, a legally acceptable representative should be involved in the decision. Special care should be taken in the studies involving children.
The authors should obtain informed consent from the study participants to publish the results and notify the editorial staff of it.
Ethics of animal use in research
When conducting experimental research in animals, the authors are obliged to include information on compliance with institutional and national standards on the use of laboratory animals.
To present more accurate and correct information about research involving animals, the editorial staff recommend following the ARRIVE guidelines . The use of these guidelines will improve the quality and reliability of published articles and allow other researchers to reproduce the results.
Ethics of research involving human subjects
We rely on the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical Association (Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects) and endeavour to ensure compliance with ethical and data collection standards for research involving human subjects. Before beginning a study, researchers should familiarise themselves with the informed consent principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and carry out the study in strict accordance with those principles as set forth below (Articles 25‒32 of the Declaration of Helsinki). When presenting the results of experimental research involving humans, the authors should indicate in the corresponding section of the article whether the procedures performed met the ethical standards described in the Declaration of Helsinki. If the study did not follow the Declaration, the authors should justify the approach chosen for the study and provide evidence that the Ethics Committee of the organisation where the study took place had approved the chosen approach.
According to the Sex and Gender Equity in Research (SAGER) Guidelines, the title and abstract of an article should indicate what sex(es) the study findings apply to (if the study involved subjects of only one of the sexes). The Introduction section of the article should reference publications that demonstrate sex-related differences (e.g., higher prevalence of the disease in one of the sexes) or the absence of such differences. The authors should indicate how possible differences were accounted for in the design of their study, whether the authors ensured adequate representation of male and female study participants, whether the authors used sex-related inclusion/exclusion criteria, and whether there were specific recommendations based on sex (e.g. mandatory contraception). If necessary, when describing the results of the study, the authors should provide preclinical and clinical data disaggregated by sex and discuss the respective results. The authors should discuss the extent to which the findings can be generalised to both sexes. If there was no analysis by sex, a rationale should be given in the Discussion section.
Publication Fees
Publication in the journal is free of charge for all the authors. The journal does not charge any fees for processing, submission, or publication of materials.
Disclosing Interest
This section is prepared according to the recommendations of WAME and ICMJE
A conflict of interest is a situation in which people have conflicting or competing interests that could influence editorial decisions and the interpretation of data in an article. Conflicts of interest can be potential or perceived, as well as real. Personal, political, financial, scientific, or religious factors can influence the objectivity of an opinion.
Conflicts of interest can cover the following areas:
- Financial. This conflict occurs when a participant in the publication process has received or expects to receive money (or other financial benefits, such as patents or shares), gifts, or favors that could influence the work related to a particular publication. Examples: research fees, consulting fees, public speaking fees, etc.
- Personal relationships. This conflict occurs in the case of personal relationships with family, friends, competitors, former colleagues.
- Political and religious beliefs. Belonging to one religion or political party may influence the outcome of a paper that addresses these issues.
- Institutional Affiliation. This conflict arises when someone involved in the publication process is directly affiliated with an organization that has an interest or disinterest in publishing material on a particular topic.
The editors may ask authors additional questions or request missing information if necessary.
Conflicts of interest may affect authors, reviewers, and editors. The following policy statements have been prepared based on the ICMJE guidelines.
Authors' Responsibilities in Disclosing Interest
When authors submit a manuscript of any type or format, they are required to disclose all relationships and activities that may influence or be perceived to influence their work by completing the ICMJE 13-item form.
The author must include information about the conflict of interest in the appropriate section of the article based on the completed ICMJE form. If there is no conflict of interest, the author must also disclose this. An example of the wording is: "The author declares that he has no conflict of interest."
Reviewers' Responsibilities in Disclosing Interest
Reviewers must inform editors of any conflicts of interest that might influence their judgment of a manuscript and recuse themselves from reviewing if there is reason to be biased.
Editors' Responsibilities in Disclosing Interest
Editors who make final decisions on manuscripts must recuse themselves from editorial decisions if they have a conflict of interest or relationships that could create potential conflicts related to the articles under consideration.
Other editorial staff involved in editorial decisions must inform editors of their current interests (as they may influence editorial decisions) and recuse themselves from making decisions if they have a conflict of interest.
Editorial staff must not use information obtained from manuscripts for personal purposes.
The articles of the editor-in-chief, deputy editors-in-chief, and members of the editorial board of the journal must clearly indicate their affiliation with the journal.
If undisclosed conflict of interest is discovered in an unpublished article, the journal's editors act in accordance with the COPE guidelines.
If an undisclosed conflict of interest is discovered in a published article, the journal's editors act in accordance with the COPE guidelines.
Plagiarism
The editorial staff of the Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine screens all the submissions with the plagiarism detection software Antiplagiat. If plagiarism is detected, the COPE guidelines on plagiarism will be followed.
Post-Publication Discussions and Corrections to Published Articles
In some cases, it may be necessary to change a published article. At the Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine, the editors support the practice of making necessary amendments to published materials and follow the COPE guidelines.
All the post-publication changes will be followed by a notification, which will always include a reference and link to the original version of the article, so that readers can be aware of any changes.
The editors use the following publicly available practices:
- Corrections
- Expressions of Concern
- Retractions
- Removal
These practices aim to ensure the integrity of published research.
Correction
Corrections are made to the article if it is necessary to correct an error or add missing information, and this does not affect the integrity and scientific significance of the article.
Corrections can be made, for example, to a figure caption, data on research funding can be added, or information about a conflict of interest can be clarified.
If such changes are made, a separate notice about the correction is published. The general algorithm of actions is as follows:
- The correction is made to the original version of the article
- A description of the change made is inserted in the Abstract field of the original version of the article
- A notice about the correction is published, which contains information about the original version of the article, as well as links to it, the names of the authors and a description of correction
Notices about the correction of spelling errors, typos, and other minor changes are not published separately. The website reports that corrections have been made to the article (without details).
Expression of Doubt
An expression of doubt is reported in the following cases:
- Serious concerns were expressed about a published article, but the investigation failed to prove anything
- For some reason, the investigation will not be conducted or cannot be completed for a long time
In such cases, it is necessary to notify readers of what is happening as soon as possible.
After the investigation is completed, the article may be amended or retracted.
Retraction (withdrawal) of an article
The journal’s editors retract an article in the following cases:
- When there is clear evidence that the results are unreliable for a number of reasons: serious errors in calculations, fabricated data, manipulation of images
- Plagiarism was detected in the article
- The results have already been published in other journals, and the author did not justify the need for re-publication and did not notify the editor
- The article contains materials and data for the use of which permission was not obtained
- Copyright was violated, the authorship included persons who do not meet the authorship criteria, or another serious legal problem arose (for example, confidentiality was violated)
- Research ethics were violated
- The peer-review process was compromised
- The author did not disclose a conflict of interest that, in the editor's opinion, could have influenced the reviewer's or editor's decision to publish the article.
When retracting an article, the editors must act according to the following algorithm:
- Conduct an investigation and verify that a retraction is necessary
- Prepare a retraction notice: include the words “Retraction” and the title of the article in the title, describe the reason for the retraction, indicate who initiated the retraction, and provide a link to the retracted article
- Publish the retraction notice
- Replace the original version of the retracted article, noting in the pdf file that the article has been retracted
- Report the retraction to the databases
- Submit information about the retraction to the database of retracted articles
The editorial board works with retracted articles according to the COPE guidelines. The procedure for retracting articles is carried out in accordance with the rules of the Ethics Committee of the Russian Association of Science Editors and Publishers (ASEP):
- If the author/authors consider it necessary to retract an article, they contact the editorial board, explaining the reason for their decision.
- If the editorial board decides to retract the article based on its expertise or the information received, the executive secretary informs the authors/authors' group of the decision. The author (contact person in case of collective authorship) will be familiar with the wording justifying the retraction of the article.
- If the author/authors' group ignores the editorial board's request, the editor-in-chief or executive secretary will seek assistance from ASEP.
- Having decided to retract the article, the editorial board indicates the reason for the retraction (in case of plagiarism, indicating the sources of borrowing), as well as the date of the retraction. The article and the description of the article remain on the journal's website as part of the corresponding issue of the journal, but the electronic version of the text is marked RETRACTED and the date of retraction, the same note is put in the table of contents of the issue.
- A protocol indicating the date of the editorial board meeting, the results of the examination, the reasoned decision and the completed form is submitted to ASEP, scientific information databases (CyberLeninka, etc.), and all online libraries and databases in which the journal is indexed.
Such form shall include the following:
- Full name of the author(s) and the title of the article
- Name of the publication from which the text is retracted
- Initiator of the article retraction
- Reason for retracting the article and the date of the decision
- Link to the page on the publication’s website that provides information about the retraction
- Article output data and DOI (if any)
- Subject (medical, pharmaceutical branches of science, etc.)
- Date of update
Removal of an article
Articles are removed from the journal only in extreme cases when it is impossible to follow the protocol for making changes, retracting an article, or expressing doubt. An article may be removed in the following cases:
- If dissemination of the article may pose a serious risk
- If the article contains content that violates the privacy of a research participant
- If the article violates someone's legal rights
- If the article is subject to removal by a court order
Updates and post-publication discussions of articles
Additions to a published article
An author may need to supplement an article some time after its publication. In such a case, the journal’s editors may publish an addition to the article. Additions to an article are subject to the same peer review requirements as the original manuscript.
When an addition is published, the file with the original version of the article is updated, and a notice about the addition to the article is additionally placed in the current issue of the journal, including information about the article, its authors, the essence of the changes, and a link to the article.
Commentary on a published article
Comments are short materials that may express an opinion or observation regarding a published article, no later than 3 months from the date of online publication. Comments are reviewed and also sent to the authors of the article so that they have the opportunity to prepare a response to the commentary, which the editors publish together with the commentary in one issue.
No more than one round of published commentary and response from the authors is allowed for one article.
The decision to publish comments is made by the editor-in-chief. The commentary and responses must cite each other, while the title of the original article must be preserved and added to it first through a colon or "Commentary on the article:" (where the first author is indicated and then the full title of the article in quotation marks) or "Response to the commentary on the article:" (where the first author is similarly indicated and then the full title of the article in quotation marks).
What should authors do if they discover an error in their article?
Authors may discover a technical or semantic error after the article has been published. In such cases, authors should notify the editors as soon as possible, especially in the case of errors that may affect the interpretation of the results or cast doubt on the intergrity. The corresponding author is responsible for reaching an agreement with authors on further interaction with the editors.
Authors who believe that changes should be made to the published article should contact the editors by e-mail: info@geriatr-news.com.
Preprint and Postprint Policy
Preprints
The Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine encourages posting preprints of manuscripts on preprint servers. A preprint is defined by COPE as a scientific manuscript that authors post on an open platform (usually before or in parallel with the peer-review process in the journal).
Publishing a preprint is not considered a duplicate publication and does not affect the editor's decision to publish in the journal.
The author should notify the journal about the posted preprint at the time of submission of the manuscript and provide a link to the preprint with the DOI identifier and the terms of distribution of the preprint.
The authors are responsible for updating the preprint record with a link to the published article. The link should include the DOI and the URL of the published version of the article on the journal website.
The original text of the preprint should not be changed based on the comments of the reviewer and editor, and the text of the preprint should not be replaced with the text of the published article, or the text of the preprint should not be removed after the publication of the article.
Postprints
The journal allows authors to independently archive and otherwise use manuscripts in two versions:
- Peer-reviewed and accepted for publication
- Layoutd and published online
To post any version of the manuscript, authors can use:
- Personal website or blog
- Social networks
- Institutional repository
- Subject repository
- Direct contact with faculty or students, passing on this version of the article for personal use.
In all cases of using an accepted or published manuscript, the author should clarify its status and provide information about the planned publication or placement with the DOI, if it has already been formed.
For example: The article “Title of the article” has been peer-reviewed, accepted for publication and will be published in No. 3 2027 of Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine.
Data Access & Reproducibility
This section of the policy has been developed based on the COPE recommendations for working with data and the Guidelines for Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) in Journal Policies and Practices.
The authors are encouraged to make research data and protocols supporting their publications publicly available, but they are not obliged to do so. The authors’ consent to grant open access to the research data will not impact the editorial decision on publishing their manuscript.
Definition of research data
Research data include any factual materials which were used in the research, recorded on any media, in a digital or non-digital form. These include tabular data, codes, images, audio- and video files, documents, maps, raw and/or processed data. This policy applies to the research data that may be required to verify study results reported in articles published in Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine. Research data include information obtained directly by the authors (“primary data”) and data from other sources analysed by the authors in their study (“secondary data”).
Definition of exceptions
This policy does not apply to research data that are not required to verify the validity of the research results reported in published articles.
Information on confidential data may be shared via publishing in research data repositories with limited access or pre-anonymisation. The authors can also grant open access only to the research metadata and/or instructions for other researchers on requesting access to the data.
Data deposition
The preferred mechanism for sharing research data is the use of data repositories. Please see the lists at https://repositoryfinder.datacite.org to find research data repositories.
Data citation
The journal encourages access to research data under the Creative Commons licences. The editorial staff do not enforce the use of open-copyright licences when data are deposited in a third-party repository. The Publisher of the journal does not claim ownership of the research data which were provided by the author together with the article.
Questions regarding the implementation of this policy may be addressed to the journal editorial depatment.
Study protocols and their registration
The journal welcomes the preliminary publication of research protocols and their registration in the applicable registers (for example, clinicaltrials.gov). For randomised controlled trials, the protocol must be registered before the authors submit the manuscript.
Advertising Policy
- The advertising policy of the journal is based on the WAME Recommendations on Publication Ethics Policies for Medical Journals and the Law of the Russian Federation “On Advertising”.
- The journal generates revenue from advertising, which creates a potential conflict of interest. Editors’ decisions do not depend on the cost of advertising or producing reprints. Advertisers and sponsors have no influence over the editor’s decisions, regardless of the terms of advertising or other agreements.
- The volume of advertising materials in the journal should not exceed 5%.
- Reprints should be published only in the form in which they were originally published in the journal (including subsequent corrections), so there should be no additions or changes in them.
- Advertisements in the journal must be related to products or drugs used in intensive care, medical education or scientific symposia.
- The content of special (additional) issues is regulated only by the decisions of the editor, sponsors or advertisers cannot influence its content. The articles in supplements underwent a standard peer review procedure.
- The functions of editor and advertising manager in the journal are separate.
- The editorial board of the journal does not accept for consideration and does not print advertising articles (both on a reimbursable and free basis).
- Commercial advertisements must not appear adjacent to any editorial or article that discusses the advertised product, nor must they contain references to the issue of the journal in which they appear.
- Advertising content must be distinguished from editorial and other materials so that the difference between them is obvious.
- The publisher does not allow any advertising campaigns to draw attention to the treatment or drugs associated with a particular article. Advertisers in the ad module cannot link to scientific articles using keywords.
- Ads must not be deceiving or misleading. Advertising should not exaggerate the actual characteristics of the advertised product. Ads must not contain offensive considerations of a religious, racial, or religious nature.
- The editors reserve the right to reject any advertising material damaging the reputation of the publisher or inappropriate to the content of the journal .
- The decision to publish an advertisement is made only with the participation of the editor and the editorial board of the journal.
Direct Marketing
The Journal's policy prohibits mass mailings to potential authors for manuscript solicitation.
Invitations to become an issue editor, author of an expert opinion or a review are sent individually by the editor-in-chief.
In any activities involving direct contact with the Journal’s potential target audience (to include conferences and exhibitions, social networks, etc.), the Journal strives to be appropriate, well targeted and unobtrusive. It also follows legislation about personal data and confidentiality, as well as professional communication standards, where the information provided about the publisher, or Journal shall be truthful and not mislead readers, authors or other potential partners.
AI Technologies
The expanding use of AI-based applications in scholarly publishing, including when preparing, writing, and reviewing scientific articles, the editors of Russian Journal of Geriatric Medicine consider it necessary to focus the attention of the authors and reviewers on the following provisions.
- Chatbots such as ChatGPT (and similar ones) cannot, under any circumstances, be listed as authors of an article or as contributors to the manuscript. AI-based applications and tools do not meet authorship criteria because they are not (and cannot be) accountable for their work, cannot declare conflicts of interest, and cannot manage copyright.
- It is not prohibited to use chatbots or other AI-based applications when drafting or reviewing a manuscript. In some cases, such applications can be used to edit text, search for additional literature, and collect and analyse data. The authors and reviewers should note that chatbots often give false information, which requires an additional verification step.
- If an AI-based application is used to draft a manuscript, the authors should specify in the manuscript the name and version of the application, as well as the prompts given. Only the authors are responsible for the text of the manuscript they submit to the journal, regardless of what AI-based applications they used and to what extent.
- When checking manuscripts, the editors use the appropriate module of the Antiplagiat system, which can detect AI-generated text.
The Journal shares the position of the international publishing community regarding the use of AI in the preparation of scientific articles, as set out in the documents of the World Association of Medical Editors (WAME Chatbots, Generative AI, and Scholarly Manuscripts) and the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE Recommendations part II, paragraph A4).

























